

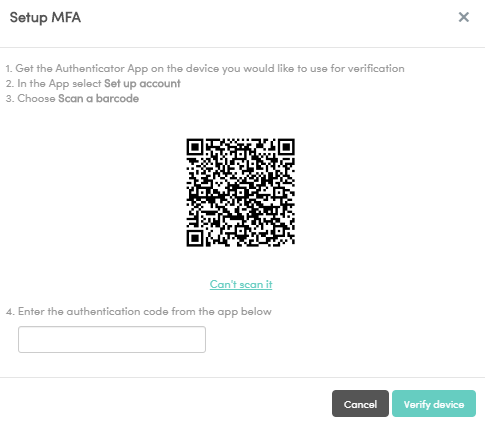
You can use security defaults in Azure AD tenants to quickly enable Microsoft Authenticator for all users. How to enable and use Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication
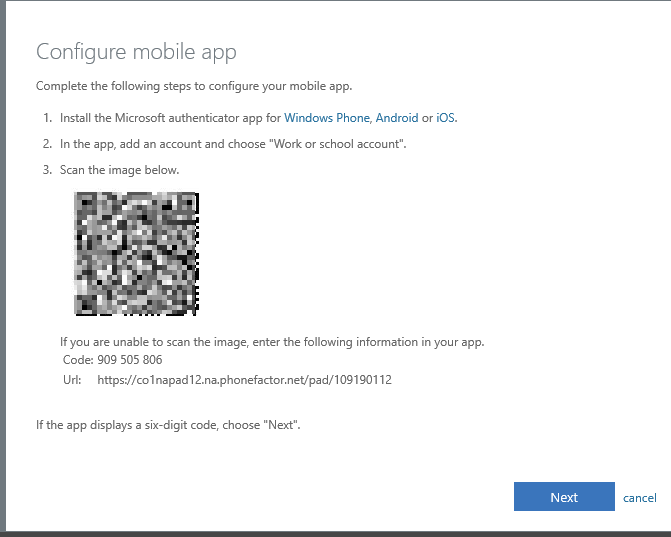
The following additional forms of verification can be used with Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication: Users can access My Profile to edit or add verification methods. When users sign in to an application or service and receive an MFA prompt, they can choose from one of their registered forms of additional verification. English is also used by default if the browser locale can't be identified. Network Policy Server (NPS) will always use English by default, regardless of custom greetings. If you use custom greetings but don’t have one for the language identified in the browser locale, English is used by default. The prompt language is determined by browser locale settings. The verification prompts are part of the Azure AD sign-in, which automatically requests and processes the MFA challenge when needed. You don't need to change apps and services to use Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication. Administrators can choose forms of secondary authentication and configure challenges for MFA based on configuration decisions. When users register themselves for Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication, they can also register for self-service password reset in one step.
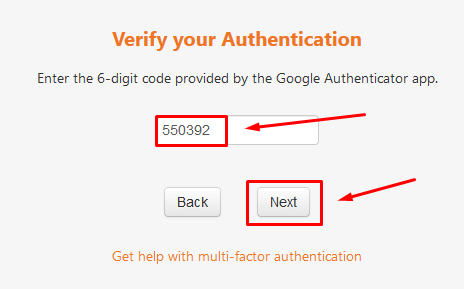
Multi-factor authentication is a process in which users are prompted during the sign-in process for an additional form of identification, such as a code on their cellphone or a fingerprint scan.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
